Assessment of Transportation Infrastructure Gaps Utilizing GIS
Leveraging AI-Powered Geospatial Data to Identify Transportation Infrastructure Gaps
Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) are pivotal in ensuring community safety and well-being by developing sustainable transportation networks. To navigate an evolving landscape and proactively address community needs, forward-thinking MPOs are increasingly turning to advanced technologies. This is exemplified by the Southeast Michigan Council of Governments (SEMCOG), which is leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance its regional planning.
This analysis examines how SEMCOG utilized AI-powered geospatial data to identify critical infrastructure deficiencies, such as unmarked crosswalks and limited sidewalk access. By adopting a strategic, data-driven methodology, SEMCOG developed targeted interventions to foster a safer and more equitable community.
The Transformative Impact of AI-Powered Geospatial Data
Envision a transportation planner analyzing high-resolution digital maps to pinpoint gaps in pedestrian infrastructure and plan new bicycle lanes that enhance neighborhood connectivity. This scenario is now a reality, as innovative organizations harness AI-driven geospatial data to revolutionize transportation planning. This technology empowers data-informed decision-making, fundamentally shaping the future of community infrastructure.
A Pioneering Initiative: SEMCOG’s Vision for Safer Streets
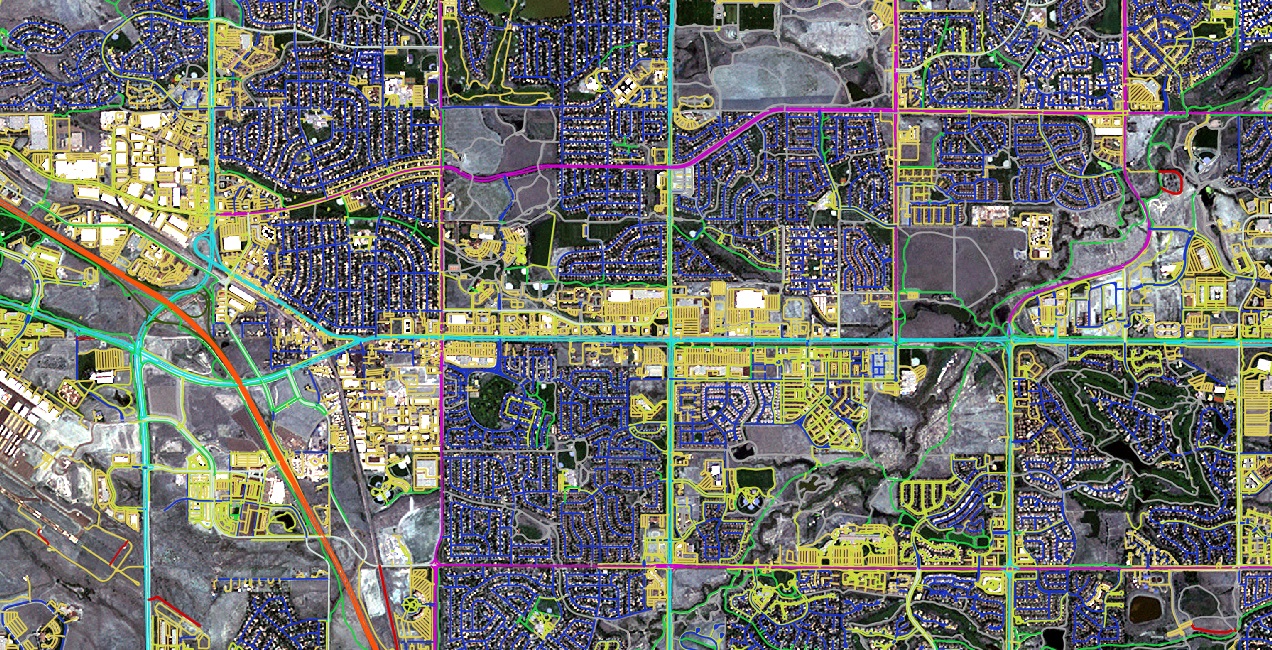
MPOs are instrumental in designing safer and more efficient transportation systems amidst challenges like population growth, diverse mobility demands, and sustainability objectives. SEMCOG has distinguished itself as a leader by adopting cutting-edge AI-powered mapping data, gaining an unprecedented, detailed understanding of its region’s transportation network.
This approach provides a high-definition perspective of transportation assets, revealing critical details like curbs, crosswalks, and sidewalks with exceptional accuracy. The outcome is a measurable enhancement in accessibility and safety, directly benefiting the region’s 4.8 million residents.
The Limitations of Traditional Data Collection Methods
Historically, MPOs have relied on geospatial data for planning, with information on sidewalks and crosswalks being crucial for compliance with regulations such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Traditionally, acquiring this data involved manually digitizing features from aerial imagery—a process that, while effective for small areas, becomes prohibitively labor-intensive and time-consuming at a regional scale.
Manually digitizing thousands of miles of infrastructure is an unsustainable task. As communities evolve, these manual methods struggle to keep pace, leading to outdated data, reliance on estimations, and reactive planning. This inefficiency hinders the proactive solutions necessary to serve growing populations effectively.
Enhancing Efficiency with AI-Powered Geospatial Data
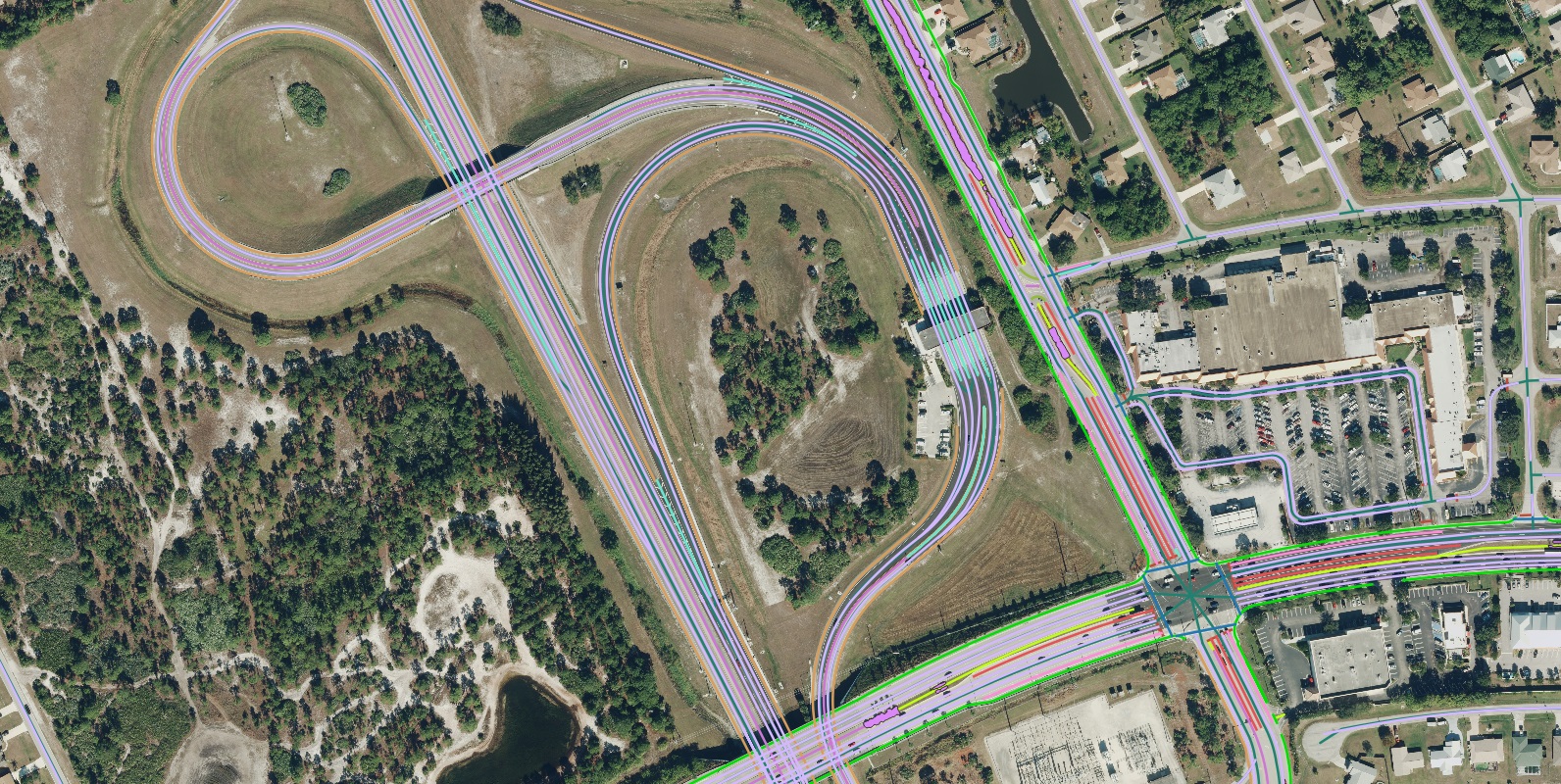
Modern AI-powered mapping technologies have revolutionized this process, eliminating the need for extensive manual digitization. team Nazru deliver highly precise vector data for transportation features—including crosswalks, sidewalks, and bike lanes—in a fraction of the time previously required. By automating feature extraction from high-resolution imagery, these systems provide comprehensive, up-to-date datasets across entire regions within weeks. This allows GIS professionals to shift their focus from tedious data collection to higher-value analysis and strategic innovation.
Driving Innovation with Advanced Data Analytics
Committed to enhancing mobility, safety, and economic development, SEMCOG serves as a model for other regions in adopting innovative solutions for sustainable planning outcomes. Serving nearly five million people across seven counties in Southeast Michigan, SEMCOG leveraged AI-powered geospatial data to advance its transportation planning initiatives. The following section details how this data was applied to assess the accessibility and safety of sidewalk networks, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the planning process.
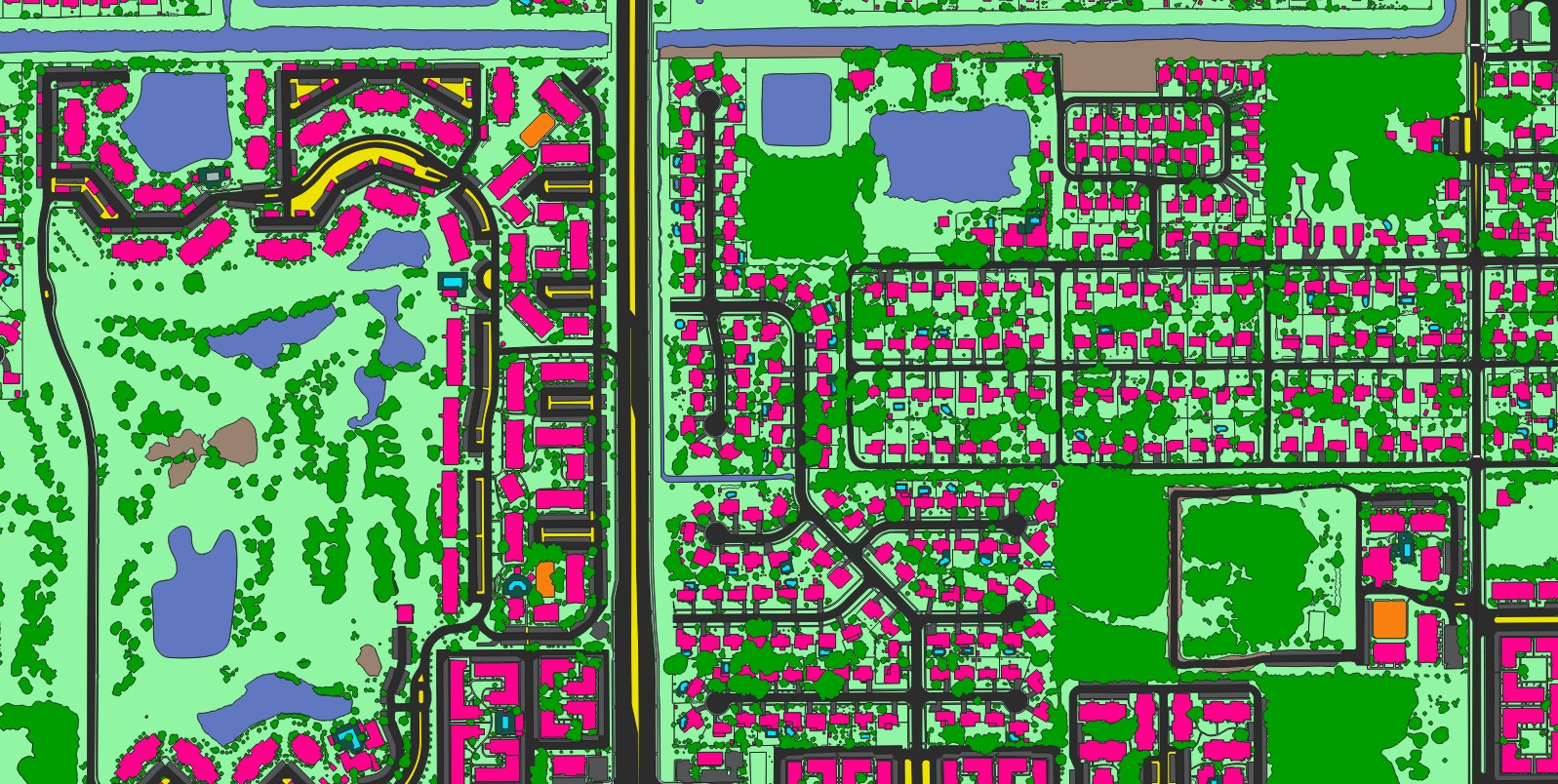
A sample of the sidewalk data extracted by Nazru AI.

Based on the success of the initial project, Nazru subsequently worked to extract a more comprehensive inventory of the region’s infrastructure. This subsequent phase involved detailed mapping of numerous features including buildings, sidewalks, driveways, roads, parking facilities, railways, pavement types, grass, bare land, trees, tree canopy, and water bodies throughout southeastern Michigan.
This rich, multi-layered dataset has been adopted by diverse stakeholders including water resource councils and municipal planning departments. It now serves as a foundational tool for supporting public infrastructure decision-making across key areas such as stormwater and flood management, pedestrian safety and traffic engineering, and green infrastructure planning.
A sample of land cover data for Annapolis, Maryland, USA digitized and classified by Nazru.













Empowered by AI-driven data, organizational leaders can now predict areas of potential stormwater accumulation, evaluate how new green infrastructure could mitigate flooding, and identify opportunities for traffic engineering to enhance pedestrian safety. This creates a powerful cascade effect: more precise data leads to more intelligent decisions, which in turn foster the development of more equitable, sustainable, and interconnected communities.
Paving the Way for Safer, Connected Communities
Envision a future where transportation planners do not merely react to changing conditions—they anticipate them. Imagine autonomous vehicles navigating seamlessly because planners had access to granular, high-precision data. Picture a city’s climate resilience strengthened by advanced geospatial insights, ensuring infrastructure investments are durable and future-proof.
The Nazru success story demonstrates that embracing innovation transcends the adoption of new tools; it is about unlocking transformative capabilities. With AI-driven geospatial solutions at their disposal, planners can confidently pursue active transportation initiatives, carbon reduction strategies, and comprehensive network-wide safety analyses. This evolution moves beyond static maps to a dynamic, living digital framework that adapts in lockstep with the community it serves. This is not merely planning—it is future-proofing.
To explore how AI-driven geospatial data can advance planning objectives in your community, we invite you to contact our team.