The Role of Maps in Data Representation
Maps have long served as a vital tool for representing data across physical space. For millennia, humans have relied on maps to communicate geographic information, such as the location and extent of rivers, mountains, and settlements. In the modern era, the advent of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has significantly expanded the applications of mapping, enabling the spatial representation and analysis of diverse datasets—including demographics, points of interest, and other location-based information.
While maps are commonly associated with identifying places and objects on Earth’s surface, they also play a crucial role in tracking changes over time and space. Known as change detection, this capability provides valuable insights into the evolution of landscapes, populations, and infrastructure. By visualizing these changes, patterns emerge that would otherwise be difficult to discern through raw data alone.
What Is Change Detection Mapping?
Change detection mapping involves the spatial analysis and documentation of features that have evolved in a specific area over a defined period. Unlike simply comparing two maps from different times, true change detection pinpoints exactly which features have changed within the area of interest.
This approach streamlines geospatial analysis by eliminating the need to manually examine every data feature. Instead, modified features are highlighted through attribute fields or as a separate GIS layer, enabling efficient visualization and further analytics. Change detection mapping allows professionals to quantify, locate, and describe transformations over time, supporting a wide range of analytical applications.
Applications of Change Detection Mapping
In today’s rapidly evolving world—marked by climate shifts, population migration, and urban development—change detection mapping is essential for maintaining accurate, up-to-date geospatial data.
While virtually any feature can be analyzed using this methodology, at NAZRU AI, we observe particularly high demand for change mapping in the following areas:
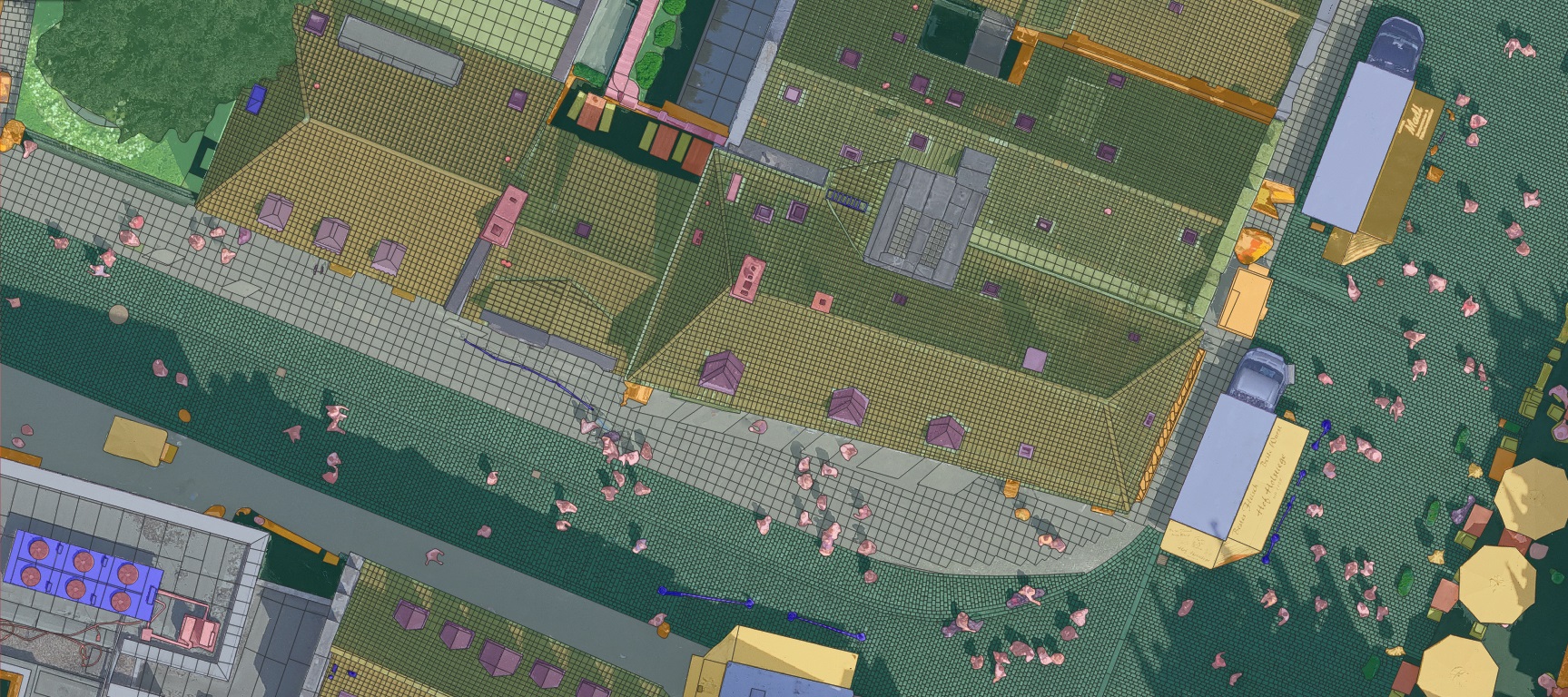
1. Building Footprints
Buildings are among the most dynamic elements of our environment. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, over 1.7 million new residential buildings were completed in February 2024 alone—not accounting for commercial, industrial, governmental, or global construction activity. Detecting changes in buildings (including new constructions, demolitions, and structural modifications) is critical for:
- Property risk assessment
- Tax valuation
- Population estimation
- Urban sprawl analysis
Change Detection Analysis: Building Footprint Evolution in Bern, Switzerland (2018-2024)


2. Impervious surfaces
Rapid urbanization drives not only building construction but also significant increases in impervious surface coverage. As communities develop, natural landscapes are progressively replaced by:
- Roads & highways
- Parking facilities
- Sidewalks & pavements
- Rooftops & built structures
This transformation fundamentally alters hydrological systems, reducing natural water absorption and increasing flood risks.
Change Detection Analysis: Road Footprint Evolution in Bern, Switzerland (2018-2024)






3. Land Cover
Monitoring changes across all land cover types is essential. Tracking variations in tree canopy, grass, shrubs, bare land, and other natural features over time provides valuable insights into deforestation, pollution, urban heat effects, and related climate concerns. Land cover change detection is significant not only for identifying the loss of natural elements but also for assessing shifts in land cover distribution within a given area. For instance, constructing a parking lot adjacent to a wetland may compromise its ecological integrity, while newly planted trees can mitigate stormwater runoff and reduce excessive sun exposure.
Change Detection Analysis: Grass and Forest Footprint Evolution in Basel, Switzerland (2018-2024)




4. Transportation Features
Highly detailed sub-classifications of individual land cover features are frequently mapped to monitor changes over time. While identifying alterations in road surfaces is useful, transportation planners often require more granular data—such as shifts in lane configurations or intersection layouts—to assess network safety, accessibility, and sustainability. Additionally, tracking modifications in sidewalk dimensions, crosswalk widths, and visibility helps evaluate whether pedestrian infrastructure is becoming safer and more accessible or deteriorating over time.
Change Detection Analysis: New-Sidewalk Footprint Evolution in Melbourne, Australia (2018-2020)

Top 5 Change Detection Mapping Applications
Change detection is a widely used geospatial technique across industries, with key applications in the following areas:
1. Insurance Risk Assessment
Property and casualty (P&C) insurers rely on change detection to evaluate risk profiles, ensuring accurate policy pricing, reinsurance strategies, and claims responses. Identifying property modifications—such as new constructions or structural additions—is critical during policy renewals, as these changes can influence risk exposure and financial outcomes.
2. Stormwater Management
Urban development increases impervious surfaces, elevating flood risks due to heightened runoff. Municipalities leverage change detection to monitor these shifts, assessing impacts on drainage systems and community flood resilience.
3. Climate Resilience
Beyond stormwater, change detection supports natural resource management, flood modeling, and green infrastructure planning. Land use changes directly affect climate resilience, influencing water quality, biodiversity, and urban heat effects.
4. Transportation Safety
Transportation planners use change detection to evaluate network demand, pedestrian infrastructure, and adjacent land cover impacts. For instance, expanding impervious surfaces near roads can increase flood risks, jeopardizing motorist safety.
5. Property Tax Assessment
Tax assessors utilize change detection to maintain accurate property records, ensuring fair taxation. Updated building footprint data reduces the need for onsite visits and captures unregistered structures.
How to Map Change Over Time
While traditional change detection was manual, AI-driven advancements now enable efficient, scalable geospatial analysis. Modern techniques empower industries to track and respond to dynamic landscapes with precision.
Change Detection Analysis: Building Footprint Evolution in Bern, Switzerland (2018-2024)




Methods for Change Detection Mapping
Change detection mapping can be performed through three primary approaches:
1. Manual Imagery Analysis
The most fundamental method involves comparing geospatial images of the same location from different time periods. Analysts visually identify changes—such as new constructions or land cover modifications—and document them manually, either directly on the imagery or in a separate record-keeping system. While straightforward, this approach is labor-intensive and prone to human error, particularly for large-scale or long-term analyses.
2. Manual Digitization
A more advanced technique involves digitizing observed changes into a structured geospatial dataset. Though this yields tangible, analyzable data, the process remains time-consuming and resource-heavy, especially when assessing extensive geographic areas or multiple time periods. Despite its drawbacks, manual digitization provides precise, customizable outputs for detailed evaluations.
3. AI-Powered Mapping
Advances in geospatial AI have revolutionized change detection by automating the process without compromising data quality. AI-driven feature extraction can rapidly digitize buildings, impervious surfaces, transportation networks, and other discernible features—while pinpointing only the changes between two datasets. This method significantly reduces time and costs, enabling organizations to scale analyses across broader regions and timeframes for deeper insights
AI-Powered Change Detection with Nazru® AI
At Nazru® AI, we collaborate with global organizations to implement efficient, scalable change detection solutions. Whether you provide your own imagery or leverage our partnerships with global data providers, our AI technology delivers accurate vector layers tailored to your specific feature analysis needs.
Ready to optimize your change detection workflow?
Contact our team to discuss your project and get started.