Leveraging GIS for Transportation Accessibility: 4 Real-World Applications
Transportation Accessibility: Building the Foundation for Equitable Communities
Transportation forms the fundamental infrastructure of our communities, creating vital connections between individuals and the essential services they need. Access to safe, reliable transportation is crucial for reaching employment opportunities, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and social activities. Despite this importance, millions of Americans face significant accessibility challenges within the nation’s complex transportation networks.
Comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date geospatial data has emerged as a critical tool for planning initiatives aimed at enhancing transportation accessibility. This analysis explores how communities are leveraging AI-powered geospatial data to evaluate infrastructure and implement meaningful improvements to create more inclusive transportation systems.
Understanding Transportation Accessibility
The US Department of Transportation (USDOT) defines transportation accessibility as “the ability of all people to reach the destinations they need to visit to meet their needs.” This concept emphasizes equitable access for everyone while specifically preventing discrimination against individuals with disabilities. An accessible transportation network enables people of all abilities to participate fully in societal activities, from employment to recreational pursuits.
Despite these ideals, transportation inaccessibility remains a widespread challenge. USDOT research indicates that nearly one-quarter of all transit stations nationwide were reported as inaccessible. Additional complications arise from inadequate sidewalk infrastructure and missing essential features such as curb cuts and crosswalks, creating further barriers to mobility.
Challenges in Acquiring Transportation Mapping Data
While detailed geospatial data is essential for achieving transportation accessibility goals, many Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) and Departments of Transportation (DOTs) struggle to obtain and maintain the necessary information. Effective evaluation and planning require highly detailed vector data capturing dynamic network elements including crosswalks, sidewalks, bike lanes, and medians.
The process of acquiring comprehensive data—such as sidewalk infrastructure with width attribution for an entire network—presents significant challenges. Historically, obtaining and maintaining this data has demanded substantial labor and financial resources from planning authorities. Some transportation departments attempt first-party data creation, but this approach often proves prohibitively time-consuming and expensive. Alternatives like open-source platforms frequently yield data that is outdated, fragmented, or lacks the necessary detail for meaningful analysis.
AI-Powered Solutions for Accessible Transportation Planning
Artificial intelligence is transforming this landscape by enabling organizations to overcome traditional data acquisition barriers. Nazru’s AI technology processes high-resolution imagery to extract precise transportation features at scale, achieving accuracy comparable to trained GIS professionals. This capability allows planners to redirect resources from manual digitization toward informed analysis, ultimately creating more accessible transportation networks that better serve diverse community needs.
Case Study: Analyzing ADA Compliance in Baltimore
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), established in 1990, provides crucial federal protections against disability-based discrimination. This legislation sets specific guidelines for transportation departments to develop and maintain accessible infrastructure, with regulations designed to enhance accessibility for individuals with visual impairments, wheelchair users, and other disabled populations.
Detailed geospatial data plays an essential role in helping planning departments assess accessibility features and ensure compliance with ADA standards. These standards specify requirements for sidewalk width, curb ramps, bus shelters, wheelchair spaces, and other critical transportation network elements. Maintaining comprehensive, accurate, and current data is fundamental to understanding existing conditions, identifying areas requiring improvement, and planning effectively for the future.
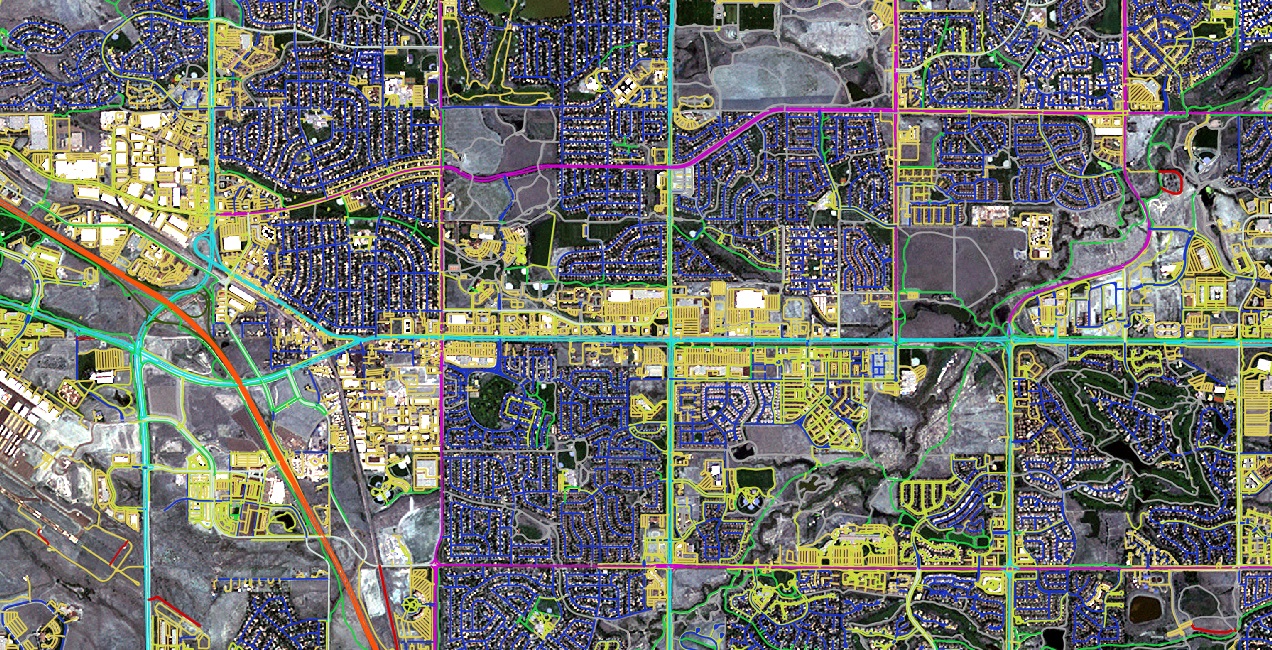
Enhancing Accessibility in Chicago through Improved Neighborhood Mobility
While manual digitization of these features would have required thousands of hours of human labor, Nazru’s AI-powered mapping technology successfully extracted them in a fraction of the time while maintaining the high accuracy standards expected from trained GIS professionals.
The dataset provided by Nazru includes 26 distinct feature classes—such as turning lanes, medians, stop lines, and crosswalks—which now serve as fundamental infrastructure for supporting inclusive transportation planning and accessibility compliance initiatives worldwide.
For instance, the interactive map of sidewalk features created from Nazru’s data has enabled the identification of critical gaps in local pedestrian networks. This precise, data-driven insight now guides the development of targeted programs to enhance neighborhood mobility and ensure safer, more accessible infrastructure for all citizens.


























A sample of advanced transportation and land cover features extracted by Nazru AI in Lindau, Germany.
Supporting Statewide Planning Initiatives with Comprehensive Geospatial Data
Beyond its applications in accessible transportation planning, the detailed geospatial dataset provided by Nazru has demonstrated significant value across multiple critical planning domains throughout the region. The data has actively supported flood management and stormwater planning initiatives, informed housing and urban development strategies, and contributed to economic development planning, showcasing its versatility as a foundational resource for comprehensive regional development.
Advancing Urban Mobility in Koln, Germany through Integrated Transportation Planning
The development of accessible infrastructure represents a fundamental commitment not only to accommodating individuals with disabilities but also to promoting safer and more sustainable transportation modes for all community members. Accessible transportation planning maintains intrinsic connections with complementary frameworks such as active transportation planning and Vision Zero initiatives.
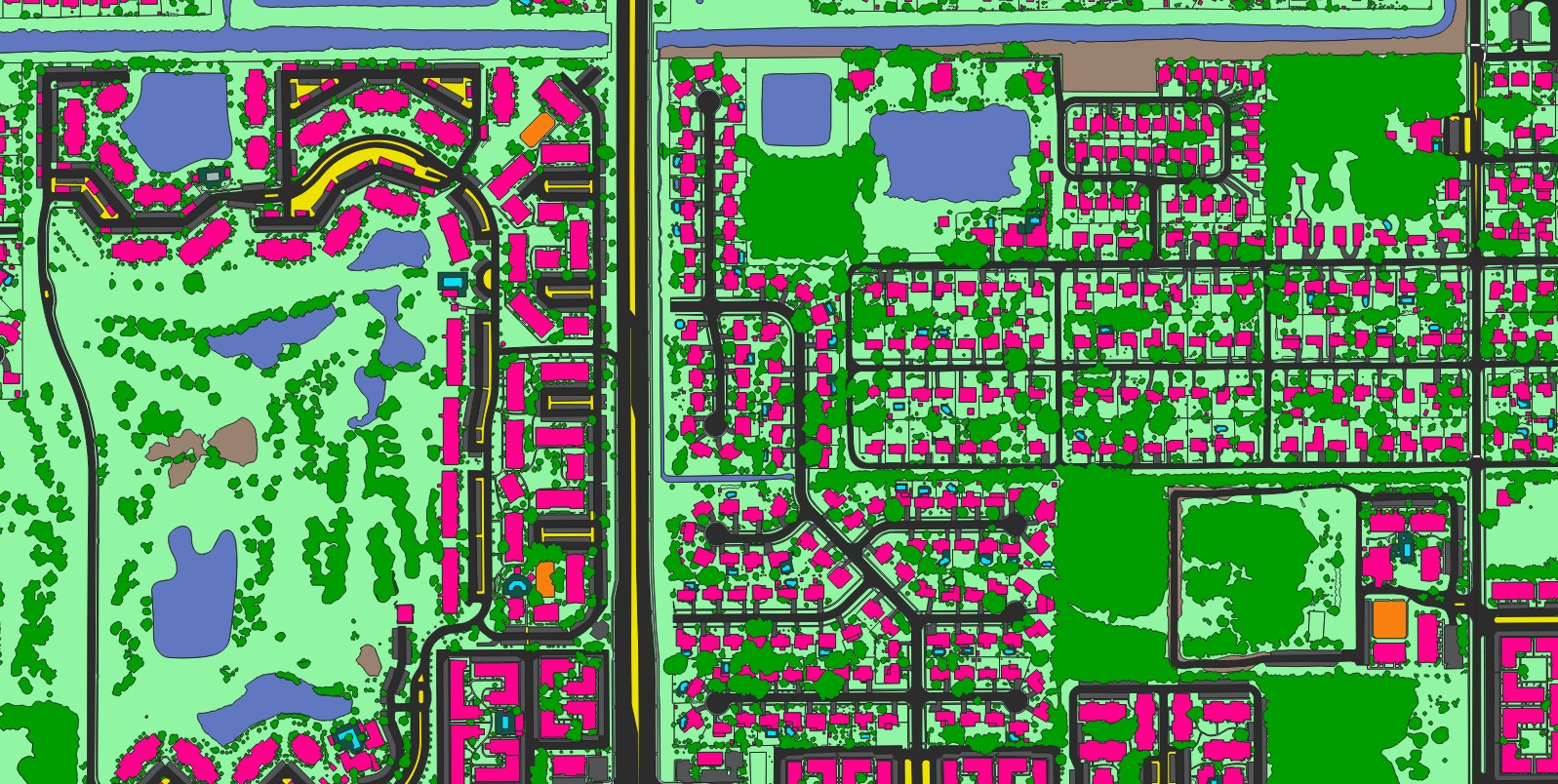
Nazru undertook a comprehensive initiative to address transportation challenges in Koln, Germany, creating a detailed geospatial dataset to support urban mobility planning. The resulting dataset included precise specifications for roadway and laneway configurations with width attributes, complete sidewalk and bicycle infrastructure networks, and numerous other critical features. These meticulously crafted right-of-way transportation planning maps provided city planners with the precise geospatial intelligence necessary to strategically advance active transportation goals, thereby ensuring the continued enhancement of both accessibility and safety across the city’s transportation networks.
The Koln project demonstrated how AI-derived geospatial data can effectively support European cities in developing integrated transportation solutions that balance historical preservation with modern accessibility requirements, while promoting sustainable urban mobility patterns.














A sample of advanced transportation and land cover features extracted by Nazru AI in Koln, Germany.
Empowering Connectivity: Multimodal Planning for Accessibility in Stuart, Florida
Effective accessible transportation planning necessitates a comprehensive strategy that strengthens connectivity across diverse transportation modes. Multimodal transportation planning systematically integrates various transit methods—including public transportation networks, cycling infrastructure, and pedestrian pathways—to establish a unified network that offers diverse, interconnected mobility solutions. This holistic methodology fundamentally improves accessibility for all community members by ensuring multiple reliable routes to essential services, employment centers, and community destinations.
The implementation of comprehensive, accessible, and secure transportation alternatives directly promotes both accessibility and equity within urban mobility systems. By providing varied travel options that accommodate different physical capabilities, economic situations, and journey requirements, municipalities can guarantee their transportation infrastructure effectively serves all demographic groups.
Geospatial intelligence forms the cornerstone for analyzing existing multimodal networks and guiding evidence-based decisions to optimize their accessibility. Through sophisticated mapping and assessment of transportation assets, urban planners can detect connectivity deficiencies, establish improvement priorities, and strategically deploy resources to develop genuinely integrated mobility systems that comprehensively address community needs.
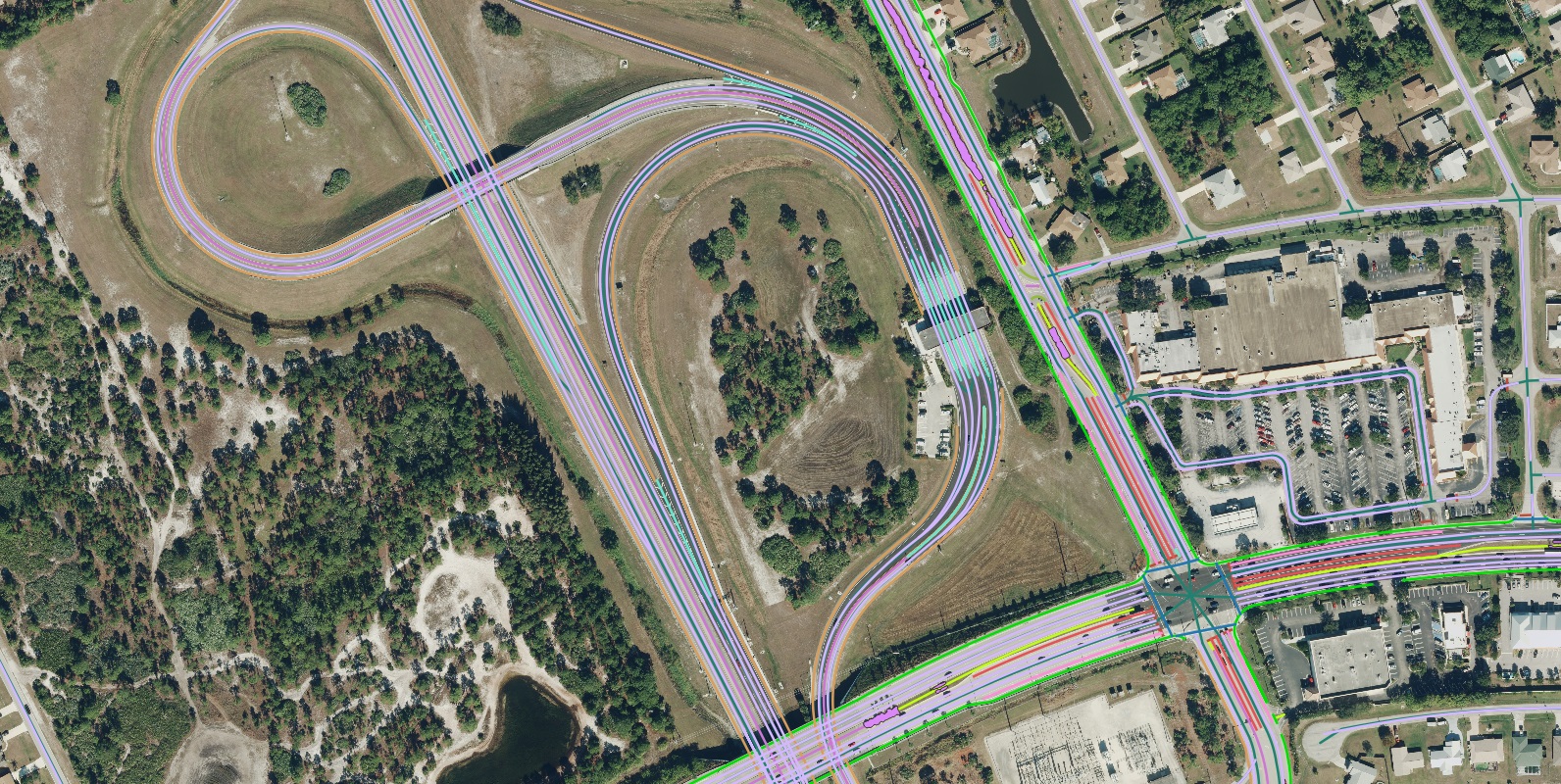
In Stuart, Florida, this data-driven framework enables planning authorities to visualize interactions between different transit modes, evaluate current accessibility metrics, and formulate targeted initiatives that reinforce the entire transportation network while specifically addressing mobility challenges faced by vulnerable populations. The approach facilitates the creation of sustainable transportation solutions that balance economic development objectives with social equity considerations, ultimately fostering a more connected and inclusive community environment.















A sample of advanced transportation features Nazru AI extracted in Stuart, Florida, California to support multimodal transportation planning.
The extraction of detailed transportation features by Nazru has been instrumental in advancing the county’s primary initiative of developing robust multimodal transportation networks. This comprehensive data infrastructure directly supports the dual objectives of enhancing community accessibility and promoting sustainable urban development, enabling planners to make evidence-based decisions that serve all residents effectively.
Advancing Accessibility with AI-Powered Geospatial Intelligence
In addressing complex transportation accessibility challenges, comprehensive, accurate, and current geospatial data serves as the foundational element for effective planning and decision-making. Nazru’s AI-driven technology provides precisely this critical infrastructure, transforming how communities identify, analyze, and resolve accessibility gaps within their transportation networks.
Take the Next Step Toward Accessible Communities
We invite you to explore how Nazru’s AI-driven geospatial solutions can transform transportation planning within your community. Our team stands ready to demonstrate how our precise, scalable data can empower your initiatives toward creating more accessible, equitable, and sustainable transportation networks.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discover how our technology can support your specific accessibility objectives.